09.09.2024 | Heading: Information
Information
28.08.2024 | Heading: Information
23.09.2024 year from 10.00 to 12.30 On the eve of World Day Against Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, the health care institution “Minsk Clinical Center for Phthisiopulmonology” will host an information and educational campaign “Stop, tobacco!»., aimed at combating smoking and raising awareness of COPD.

The purpose of the campaign is to increase public awareness regarding the harmful health consequences of tobacco consumption and exposure to tobacco smoke, formation of civil society support for measures, aimed at combating tobacco consumption, creating conditions to protect the health of citizens from the effects of environmental tobacco smoke in accordance with the Decree of the President of the Republic of Belarus and the provisions of the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control. Read completely »
Monkeypox!
27.08.2024 | Heading: Information
 Monkeypox is an acute viral disease, which appears as a rash all over the body, enlarged lymph nodes, feeling of chills and heat, headache, aching muscles and joints. Most often transmitted through close body contact and inhalation of particles of contaminated sputum and saliva..
Monkeypox is an acute viral disease, which appears as a rash all over the body, enlarged lymph nodes, feeling of chills and heat, headache, aching muscles and joints. Most often transmitted through close body contact and inhalation of particles of contaminated sputum and saliva..
The virus enters the body through the upper respiratory tract, skin and mucous membranes. It first develops in the cells of the small bronchi, bronchioles, skin and mucous membranes, where in the lower layers it continues to reproduce. From here the virus enters the crib - primary viremia occurs. The virus is absorbed by immune cells of internal organs, in which it can also persist and reproduce.
Signs and symptoms Monkeypox usually appears within a week, but can begin 1-21 days after infection. Симптомы болезни обычно сохраняются 2–4 недели, but may last longer in people with weakened immune systems.
HOW TO PREVENT LISTERIOSIS
27.08.2024 | Heading: Information
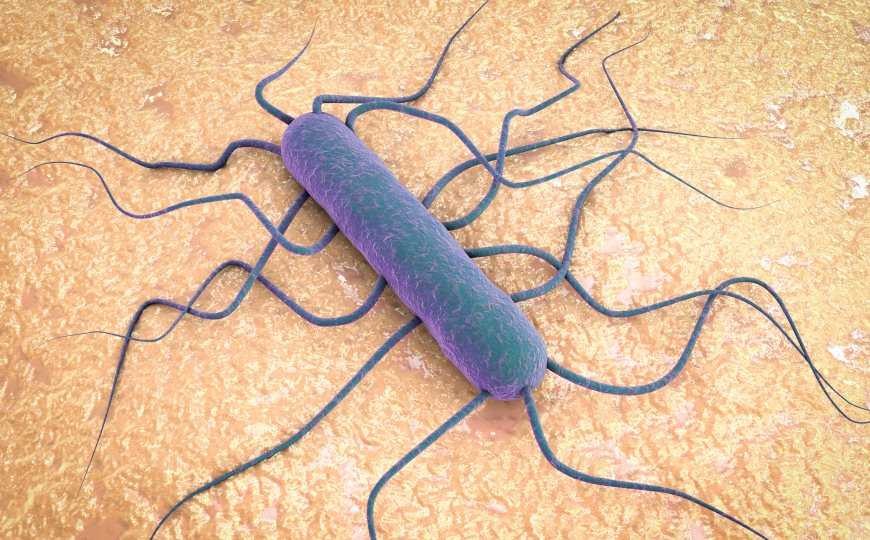 Listeriosis – infectious disease of humans and animals, is widespread. Sources of listeriosis in humans include many species of wild and domestic animals., including rodents and birds. Sick animals contaminate the environment with their secretions, soil, household items, as well as food and water.
Listeriosis – infectious disease of humans and animals, is widespread. Sources of listeriosis in humans include many species of wild and domestic animals., including rodents and birds. Sick animals contaminate the environment with their secretions, soil, household items, as well as food and water.
Listeriosis pathogens – microorganisms (listeria), stable in the external environment. They not only last a long time, but also reproduce in food products at low temperatures, even in a refrigerator. Boiling and household disinfectants have a detrimental effect on Listeria..
































Comments (1) (0) »