Extrapulmonary tuberculosis. Pott's disease.
04.04.2023 | Heading: Information
Helping the General Practitioner.
Extrapulmonary tuberculosis is usually the result of hematogenous spread of the pathogen. Sometimes the infection is transmitted directly from an adjacent organ. Symptoms vary depending on the location of the process, but usually includes fever, malaise and weight loss.
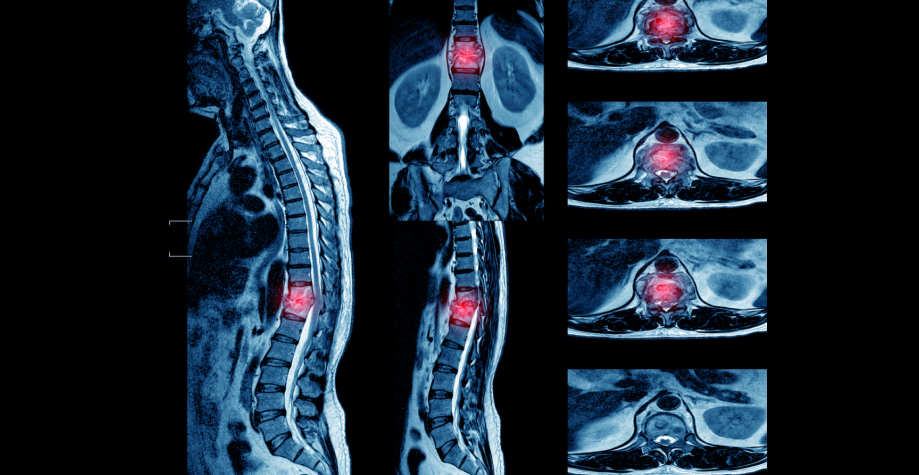
Tuberculous spondylitis (Pott's disease) is an inflammatory disease of the spine, a characteristic feature of which is the primary destruction of the vertebral bodies, followed by deformation of the spine. Tuberculous spondylitis ranks first among all localizations of osteoarticular tuberculosis, accounting for 50–60% of the total number of patients. Men suffer from spinal tuberculosis more often, than women, on average in the ratio 55:45. According to the localization of the lesion, the thoracic (60%), on the second - lumbar (30%) spine. The frequency of lesions of the cervical and sacral regions is 5%.
Clinical symptoms are very poor and often vague.: fatigue, awkwardness, stiffness, transient local pain in the affected spine, felt mainly after a long walk, when lifting a weight, jumping, run. The hidden period lasts from 3 month before 3 and more years. During this period, in 50–80% of cases, the diagnosis of tuberculous spondylitis is not even suggested.. Patients are treated mainly with a diagnosis of osteochondrosis of the spine or sciatica. Radiological examination is rarely performed at this stage of the disease., however, X-ray tomography, especially CT and MRI, allows to detect even a small primary tuberculous osteitis in the vertebral bodies.
Progressive spondyloarthritis is diagnosed with the transition of tuberculous granuloma to an adjacent vertebra and surrounding soft tissues with damage to one spinal motion segment without pronounced functional disorders. There are signs of tuberculosis intoxication: decreased appetite, sleep disturbance, intermittent subfebrile condition. There are local pains of a dull, boring nature, decreasing at rest, or diffuse pain along the spine, restriction of movements in it, posture disorder, back muscle tension, muscle stiffness, extending in both directions from the affected area of the spinal column to the angle of the shoulder blades, there is a bellied protrusion of the spinous process of the upper affected vertebra and retraction of the lower. Localized abscesses appear. Load on the spine along the axis, palpation of the protruding spinous processes and paravertebral points at the level of the lesion is painful. The spread of the process occurs through further contact destruction of the vertebral bodies and through intermuscular and interfascial spaces with the formation of pre- and paravertebral abscesses. In the absence of adequate treatment, the process acquires a chronic destructive character.. The process is characterized by an extensive area of destruction of two or more spinal motion segments with impaired support function and severe complications.. The increase in destruction leads to a decrease in the height of the bodies of the affected vertebrae, severe deformity of the spine, spinal cord compression. The most severe spinal disorders are observed when the spinal cord is compressed by sequesters and displaced posterior sections of the bodies of the affected vertebrae.. Can develop spinal disorders with dysfunction of the pelvic organs, with ascending urinary tract infection. In these cases, the addition of pyelonephritis and sepsis is possible.. The phase of exacerbation and progression can proceed for a long time, but then the sharpness gradually subsides and the phase of the fading process begins (remissions). It is characterized by an improvement in the general condition and a significant decrease in local symptoms of inflammation with the normalization of laboratory parameters.. Clinically and radiologically detectable remission is not a cure. Encapsulated caseous necrotic bone foci subsequently serve as a source of new outbreaks and exacerbations of the disease with progressive destruction.
Tuberculous spondylitis, first developed in adults, may present as an isolated lesion of one or more vertebral bodies. These lesions are rare in adults.: due to mild pain syndrome, radiation examination at this stage in adults, usually, do not fulfill. More often isolated lesions (osteitis) are identified as concomitant with the development of the process at another level. Tuberculosis lesions of the elements of the posterior vertebral column are quite rare.. More often than others, destruction of the spinous processes occurs. Less common are isolated lesions of the arches or facet joints., the possibilities of CT in these cases are indispensable. Tuberculous osteitis of the vertebral body on the radiograph has a round or oval shape, delimited by a narrow sclerotic rim, can occupy almost the entire vertebral body, contain dense inclusions. Compression of the vertebral body is possible on the basis of an extensive defect in its bone tissue due to focal destruction. Sometimes the process extends to the arches of the vertebra. In most cases, osteitis is complicated by paravertebral abscesses., expressed to varying degrees. Much more often, tuberculous osteitis of the vertebrae is detected when the horizontal end plate is destroyed and the intervertebral disc is involved in the inflammation zone with its degeneration or partial destruction..
Progressive tuberculous spondyloarthritis is characterized by destruction of the intervertebral disc. The transition is carried out by the spread of tuberculous granuloma from the initially affected vertebra to the adjacent one through the intervertebral disc in the area of the nucleus pulposus, followed by melting of the entire disc. Vertebral destruction has a deep, often subtotal character, which is due to the primary focal nature of the lesion and is an important differential diagnostic sign. Paravertebral abscesses are constantly observed, they can move into neighboring anatomical regions. Epidural abscesses are found in 75% cases of damage to one segment of the spine.
Tuberculous spondylitis in 3–14% of cases is complicated by a fistulous process, while the external fistulous opening can be at a considerable distance from the focus of destruction. Fistulography reveals the length of fistulous tracts, connection with foci of destruction, the presence of purulent streaks and internal fistulas, opening into the bronchi, intestines and other organs. In some cases, fistulography does not allow to reliably determine the location of the fistulous tract relative to bone structures., especially with simultaneous damage to the anterior and posterior columns of the spine. In these cases, stereo fistulography is performed..
In progressive tuberculous spondylitis, the characteristic changes are deep foci of destruction in adjacent surfaces of the vertebral bodies., in the destructive cavity - pus, granulation, sequestration, remnants of a broken disk. The remaining cancellous bone is broken. Abscess surrounds lateral, anterior and posterior vertebral bodies. With the defeat of three or more vertebrae, the changes are more pronounced. However, recently, thanks to new methods for detecting pathology in the spine, early use of modern antibiotics, the predominance of a productive tissue reaction of inflammation, the macroscopic picture of tuberculous spondylitis became similar to that in hematogenous osteomyelitis of the spine. A small destructive cavity is found in adjacent vertebrae, surrounded by moderately sclerotic bone, containing granulations or scar tissue. Granulations most often penetrate into the lumen of the spinal canal along the intervertebral disc. Sequesters are less common.
Laboratory diagnostics. It is necessary to exclude spondylitis in a patient with new or worsening pain in the neck or back, accompanied by an increase in ESR or CRP levels, fibrinogen.
In the absence of absolute evidence of the tuberculous nature of spondylitis, the diagnosis is established by a combination of clinical and radiation, laboratory data, tuberculin diagnostics, macroscopic intraoperative picture and the effectiveness of anti-tuberculosis therapy. Differential diagnosis of tuberculous spondylitis is carried out with inflammatory, tumor, systemic, degenerative-dystrophic diseases and traumatic injuries of the spine.
Diagnosis and treatment of this pathology is carried out by employees of the health care institution "Minsk Clinical Center for Phthisiopulmonology".
Traumatologist-orthopedist
health care institutions
Minsk Clinical Center
фтизиопульмонологии» Александр Николаевич Крук






























